Last Updated on October 21, 2025 by
Iron Deficiency anemia
Iron Deficiency anemia :
Since then, iron Deficiency anemia became the leading single nutritional risk factor and accounted > 3% of all disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) lost. Iron-deficiency anemia (IDA) is associated with deviant behavior and developmental delays in preschool (1-5 years) and infants (0-12 months) and included
The brain and body growth of both preschoolers (ages 1–5 years) and newborns (ages 0–12 months) results in behavioral abnormalities along with developmental delays when they suffer from iron-deficiency anemia. Following are few conditions:
a. Decreased motor activity.
b. Less social contact
c. Poor development of the brain
d. Diminished focus on duties
These delays in development may continue past the age of five, or school age. The fastest rate of bodily and brain growth occurs in children from ages 6 to 24 months during which time maximum iron deficiency happens. The iron supplementation is required since it is impossible to find it only through diet. Iron supplements must start two to three months sooner if your child weighed less than 2,500 grams at birth.

Suggestions for Preventing Your Child from Being Iron Deficiency anemia
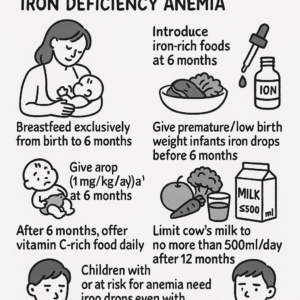
Breastfeeding your baby exclusively from the first six months onward should be promoted as a breastfeeding-only approach that avoids any complementary feeding or artificial additions.
When a child is six months old there should be introduction of iron-rich foods.
Given that diet alone is insufficient to meet the need, iron drops (about 1 mg/kg per day of elemental iron) are introduced as a supplement at 6 months of age.
Before six months, you should start giving your infant iron drops if they were born prematurely or with low birth weight.
With solids, from six months you should be giving vitamin C rich food (fruit, vegetables or juice), as these aid in absorption of iron if consumed daily, ideally alongside meals.
You should give babies cow’s milk during the first 12 months. It is also helpful when the child is over one year of age to then remind parents not to provide more than 500ml of cow’s, goat or soy milk to avoid excess, which can also contribute to iron deficiency.
Children who have anemia (Iron Deficiency Anaemia). Even those who do not have anemia (Iron Deficient Non-Anaemic) may be iron deficient. Iron drops are necessary even if your child’s hemoglobin level is normal. Since iron shortage can still affect a child’s capacity to think clearly.
FAQs:
Q1. Why is iron so vital in the development of both infant children as well as toddlers?
Ans. Young children need iron to develop normally and grow their brains as well as develop strong blood cells.
Q2. What are the principal symptoms of Iron deficiency anemia?
Ans. The main symptoms of iron deficiency in children include pale skin appearance while showing signs of fatigue with poor appetite and decrease in weight gain along with irritability and delayed cognitive development.
Q3. What techniques to be adopted, so that my baby can get sufficient iron.
Ans. Make sure your child receives adequate iron from pureed meats and fortified cereals along with lentils and spinach with approval from your pediatrician about supplements for Iron Deficiency anemia.
Q4. Exclusive breast milk provides sufficient Iron Deficiency anemia for development during the period beyond 6 months of age.
Ans. No. Breast milk cannot support a baby’s increasing iron needs during the sixth month thus extra dietary iron becomes vital.
Q5. What stands as the most suitable food source of Iron Deficiency anemia for children aged 6–24 months?
Ans. Pureed meat, chicken, fish and iron-fortified cereals together with beans, peas and spinach and egg yolks function as the best iron sources for children.
Q6. Should my child start taking Iron Deficiency anemia supplements according to doctor recommendation?
Ans. The recommendation requires medical expert approval. Supplements are recommended by health care provider when a child has high risk or developing deficiency.
Q7. Does taking vitamin C increases the body’s ability to absorb iron ?
Ans. Yes, consuming vitamin C through oranges strawberries and tomatoes enables your body to better receive absorbed iron.
Q8. Can too much iron be harmful?
Ans. Yes. Because taking in too much iron can harm your health, it’s important to turn to your pediatrician for the best advice.
Q9. Among children who are most vulnerable to developing iron deficiency which group does this risk apply to?
Ans. Yes. The highest risk group includes both premature babies and post-6-months breastfed infants who receive only breast milk and fussy eaters who show picky eating habits.
Q10. How frequently should my child be evaluated by pediatricians regarding the level of iron?
Ans. The screening procedure for iron deficiency anemia occurs between 9-12 months according to pediatric standards but additional testing may start earlier to evaluate high-risk cases.
Guideline of WHO for Iron Deficiency and its link as mentioned below: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/204712/9789241549523_eng.pdf
Thanks and Regards
About the Author – “Mr. Bibhu Ranjan Mund”, Master in Public Health (MPH) from IIHMR University, Jaipur (Rajasthan) has experience of 18 years in Public Health activities. Through “Lovely Health Tips-2025”, we share the evidence & experienced based health & wellness guides with solutions for every day well-being. More from Author
Disclaimer
This information is suggestive only and not a replacement for medical advice. For more detail, please visit to my website as mentioned below: