Last Updated on October 21, 2025 by
Early Childhood in India: Every child requires early childhood age to develop their cognitive abilities and social bonds as well as their physical attributes.
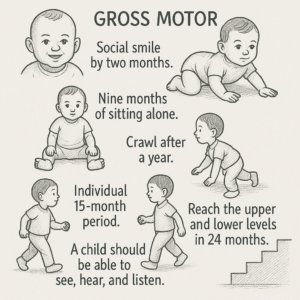
Gross Motor :
Social smile by two months.
Four months of head holding.
Nine months of sitting alone.
Crawl after a year.
Individual 15-month period.
18 months of walking alone.
Reach the upper and lower levels in 24 months.
A child should be able to see, hear, and listen.
Fine Motor and Early Childhood in India
Six months, grasp the rattle.
By the age of nine months, the child is expected to move items between his or her hands.
Twelve months of pincer grasp.
At 15 months, putting toys or other things inside a container.
By 18 months, Scribble
By 24 months uses hands or spoon to self feed.

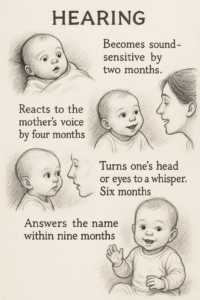
Hearing :
This becomes sound sensitive at two months.
He/she responds to the voice of the mother at the age of four months
Turns one’s head or eyes to a whisper. Six months.
Answers the name within nine months.
Speech with Language problem – Early childhood in India
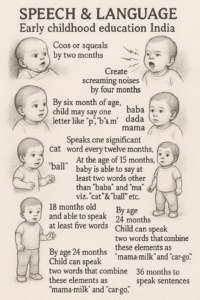
Coos or squeals by two months
- By four months provide scream like sounds
- By six month of age, child may say one letter like “p”, “b” & “m”
- At 9 mth of age of child, s/he may be able to say one word like baba, mama & kaka etc.
- Says but one notable word Twelve months to-day
- Baby during 15 months of birth, may be able to say two words other than : baba & ma like cat & ball etc.
- At about 18 mth old, babies are able to tell at least 5 different words
- By age 24 months Child can speak two words that combine these elements as “mama-milk” and “car-go.”
- 36 months to speak sentences
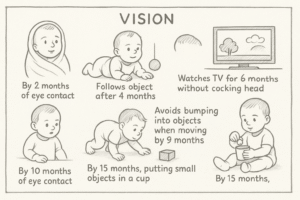
Vision :
By two months of eye contact
Four months after the object
It takes the Watches six months to cock his head at the television.
Learn not to bump into every point during the nine months of movement.
At 15 months, income into a cup of small items
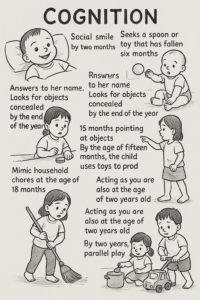
Cognition :
social smile by two months
reaches out for something six months in advance.
Poor hands by four months
Seeks a spoon or a six-month-old toy that has fallen
Her name is answered within nine meters
Reacts to no command within a year of birth
Searches hidden objects at the end of one year.
15 months pointing at objects
By the age of fifteen months, the child uses toys to pay by pulling or prodding.
Mimic household chores at the age of 18 months
Acting as you are also at the age of two years old.
By two years, parallel play
Skipped three years of play.
Features of Mental retardation : Early childhood in India
- A Slow Reaction
- Impossibility to be able to understand quickly
- Lack of Clarity
- Inability to Learn Fast
- The inability to make a decision
- Focus problems
- Short-tempered
- Unable to Recall
- Insufficient Coordination
- Development Delay
SOCIAL DEVELOPMENT : Early childhood education India
Social smile by 2 months
By six months of age, child Enables parents to choose arms
Able to Peek-a-boo by nine months of age
And knows it must distinguish between the familiar and the unfamiliar faces by one year.
At the age of 15 month, a baby can be able to imitate different phrases like “bye bye” & “namaste”.
24-month parallel play
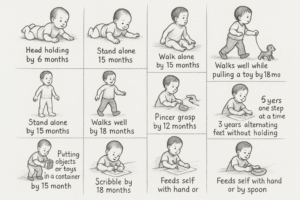
Head holding by 4 months & Rolls over by 6 months :
Sit alone by 9 months
Crawl by 12 months
Stand-alone 15 months
In Indian context most of the children walk alone by 15 months and stand alone by 12 months,
What does walking alone mean for mothers ?
At between 12 months and 15 months they walk alone by 15 months
Walks well means he can walk while pulling a toy by 18 months :
2 years one step at a time with holding
Able to Climb upstairs & down stairs easily:
3 years alternating feet without holding
Hold rattle by 6 months :
•Grasps an object with the center of his or her palm, using his thumb and the whole palm
Pincer grasp by 12 months.
Once they reach 9-months, they start being able to move objects from the palm of one hand to the other.
Placing any types of objects or playing toys in a container during 15 months of age.
Scribble by 18 months
Able to feed self in his/her hand or through spoon during 24 months
Pattern of child development (Flexion to extension):
FAQs:
Q1. What is ECD-early childhood development?
Ans. The medical field describes early childhood development (ECD) as the physical along with emotional and social and cognitive growth that occurs between birth up to approximately 8 years of age. From the moment of birth until reaching approximately 8 years old children experience physical as well as emotional and social and cognitive advancement.
Q2. Why ECD important?
Ans. Early childhood development excellence allows individuals to achieve life success with good well-being throughout their entire lives.
Q3. The fundamental domains which make up early childhood development consist of what four categories?
Ans. As below for Early childhood
- Motor activities like movement, motor skills etc.
- Cognitive development viz. thinking, problem solving etc.
- Emotional development socially i.e. relationships with other members, feelings etc.
- Development in Language in children like speaking, understanding
Q4. The early childhood development relies largely on what dietary intakes the children will consume?
Ans. The proper development of the brain along with physical growth depends heavily on good nutrition because it also strengthens immunity and prevents both present and future developmental problems.
Q5. What is the important role of parent in ECD?
Ans. Early childhood development greatly depends on parental involvement which consists of what specific roles parents should play. Children receive emotional backbone plus stimulation and nutrition from parents while their safety needs are met along with opportunities to learn from playful activities and interactive conversations.
Q6. What indications signal that a young child is developing healthily?
Ans. As below for Early childhood
- Meeting milestones viz. walking, talking
- Always curiosity with topics with engagement
- Socially active
- Communicating and development of skill
Q7. When parents be alert about developmental delays of their child?
Ans. Parents should become concerned about developmental delays which arise when their child fails to reach specified milestones during appropriate periods of their growth. Parents must bring their child for early professional evaluation with pediatrician or specialist when major developmental milestones such as walking at 18 months or using simple speech at 2 years are missed.
Q8. What are the limited mechanisms early learning institutions are following to aid young learners at the developmental levels?
Ans. These play activities are helpful for children at preschool as they improve their social skills, thinking, emotional control and prepare for entering kindergarten.
Guideline of WHO for Early Childhood development and its link as mentioned below: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/97892400020986
Thanks and Regards.
About the Author – “Mr. Bibhu Ranjan Mund”, Master in Public Health (MPH) from IIHMR University, Jaipur (Rajasthan) has experience of 18 years in Public Health activities. Through “Lovely Health Tips-2025”, we share the evidence & experienced based health & wellness guides with solutions for every day well-being. More from Author
Disclaimer
This information is suggestive only and not a replacement for medical advice. For more detail, please visit to my website as mentioned below:


1 thought on “Early childhood in India & Growth of a child”