Last Updated on October 21, 2025 by
Iron Deficiency Causes Anemia
Introduction:
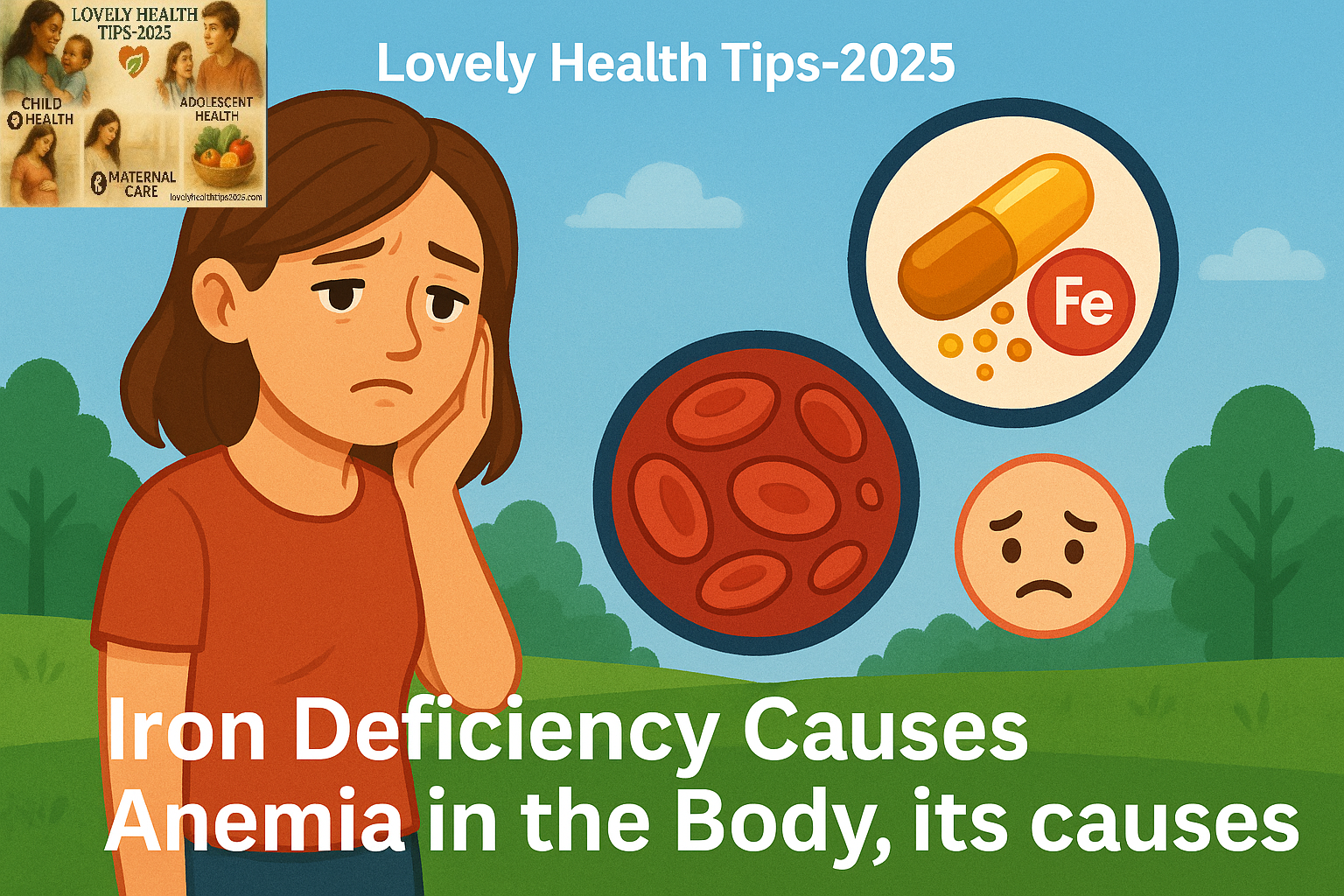
Iron Deficiency Causes anemia: It is a medical condition in which the adequate size and colour of the Adequate number of RBCs (Red Blood Cells) or the oxygen carrying capacity of the Adequate number of Red Blood Cells is less to meet the physiological needs of the body.
Iron, folic acid, vitamin C, protein, and vitamin B12 create thick red hemoglobin.
Skimpy on these nutrients makes the hemoglobin thin, pale and diluted.
It can be defined as the deficiency of red blood cells or hemoglobin in the blood
Cut off levels of Hemoglobin in human body and Iron Deficiency Causes Anemia
| Age Groups | No anaemia | Mild | Moderate | Severe |
| Children with age 6 to 59 mths | greater than 11 mg/dl | 10 to 10.9 mg/dl | 7 to 9.9 mg/dl | less than 7 mg/dl |
| Children with 5 to 11 yrs | greater than11.5 mg/dl | 11 to 11.4 mg/dl | 8 to 10.9 mg/dl | less than 8 mg/dl |
| Children with 12 to 14 yrs | greater than12 mg/dl | 11 to 11.9 mg/dl | 8 to 10.9 mg/dl | less than 8 mg/dl |
| Non pregnant women (15 yrs & above) | greater than12 mg/dl | 11 to 11.9 mg/dl | 8 to 10.9 mg/dl | less than 8 mg/dl |
| Pregnant Mother | greater than 11 mg/dl | 10 to 10.9 mg/dl | 7 to 9.9 mg/dl | less than 7 mg/dl |
| Men | greater than13 mg/dl | 11 to 12.9 mg/dl | 8 to 10.9 mg/dl | less than 8 mg/dl |
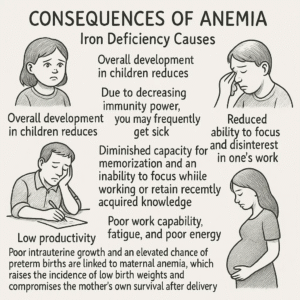
Impact & outcome of Anemia : Iron Deficiency Causes Anemia
- Overall Development Children reduces
- Due to decreasing immunity power, you may frequently get sick
- Reduced ability to focus and disinterest in one’s work
- Reduced ability to memorize and lack of focus during working and memory of the newly learned materials.
- Poor academic achievement
- Poor work capability, fatigue, and poor energy
- Low productivity
- Poor intrauterine growth and an elevated chance of preterm births are linked to maternal anemia, which raises the incidence of low birth weights and compromises the mother’s own survival after delivery.
i. CHILDREN & ADOLESCENTS :
- Decreasing academic performance, Poor memory power, attention & focus, overall cognitive function etc.
- Immunity power decreases and infections arising frequently.
- Poor results for motor development
- Irregular menstruation Exhaustion/breathlessness
- Low stamina
- Child mortality
ii. Adults :
- Disabilities, weariness, and diminished muscle strength,
- Physical activity & work productivity also decreases
- An irregular heartbeat
- Cardiac arrest
- Irritability or mood swings
- Hospitalizations
- Increased chance of mortality
iii. Pregnant Women :
- Early birth
- Low birth weight
- Blood loss during delivery
- Bleeding after giving birth
- Deaths from pregnancy
- Perinatal care
- Neonatal care
- Low immunity for which depression and morbidity increases
iv. Lactating Women :
- The quality of life
- Fatigue
- Fyspnea and heart palpitations
- Risk of infection
- Depression & Stress increases
Iron Deficiency Causes anemia
A)Nutritional: deficiency of these nutrients due to
- Low Dietary intake of iron
- Low bio-diversity
- Tea with meal
- Calcium phosphate supplement with meal
- Phytic acid and fibre in bran of cereals
- Phosphvitin in egg
B)Blood loss or destruction of blood cells due to :
- Malaria
- Delivery
- Parasitic (Hook/round worm) infestation
- Blood loss during
- Menstruation
- During adolescence & pregnancy iron needs are very high
Nutrition:
Lack of iron
Lack of folic acid
Deficiency of vitamin B12
Deficiency in vitamin A
Malnutrition of protein energy
Genetic hemoglobin disorders :
- Thalassemia
- Sickle-cell anaemia
Non -Nutritional Causes :
- Helminths spread by the soil
- AIDS
- Malaria
- Tuberculosis
- Fluorosis
- Pregnancy and early marriage
- Small intestinal problems and mal-absorption
- Poor sanitation and hygiene

Approximately Fifty percent of Anemia may be due to Iron deficiency
Inter-generational Life Cycle of Anemia : Iron Deficiency Causes Anemia
a. Women with anemia who are pregnant
b. Low hemoglobin and iron levels in a baby
c. Anemia identified during early childhood, but not treated.
d. Teenage girl with the condition of menstrual blood loss and low iron levels and hemoglobin levels
e. Because of low iron reserves, adolescents have to enter this reproductive life phase.
Methods to Manage Iron Deficiency Anaemia: Iron Deficiency causes anemia
- Food-Based Method
Boost the amount and caliber of your diet - Enhancement of food
- Supplementing with IFA and
- De-worming
- Preventing malaria
- Family planning
Counselling on different types of Nutritional Diversification methods : Iron Deficiency causes anemia
- Green fruits and vegetables
- Fish, meat, liver, and eggs
- You can eat dried fruits, sesame, jaggery, sprouting pulses, ground nuts, jowar, bajra and wheat.
- Vitamin-c rich food in our diet increases the chance of more Iron absorption. Vitamin C rich fruits are oranges, lemons, apples, pears & Indian gooseberries (Amla).

Increased consumption of Iron Rich and Iron-Fortified food is necessary, as it is dietary diversification
- Long term approach
- Involvement of people in their eating habits
- Nutritional awareness & proper education to be provided to public & community.
- Reduce inhibitor and raise promoter concentrations to improve iron absorption
Suggestive Link for Iron Tab. from Amazon as mentioned below:
A small video from youtube on this topic is as mentioned below: https://www.youtube.com/embed/tG4b3eU1Nzc?si=RGQg6Ax7YEwS1bJP
FAQs :
Q1: Iron-deficiency anaemia – meaning?
Ans. Iron deficiency anemia: If the body unable to produce adequate hemoglobin in red blood cells. If blood does not supply enough oxygen to the body tissues, it causes fatigue and a range of other issues.
Q2: Why does iron deficiency commonly cause people to become anemic?
Ans: The main reasons leading to iron deficiency anemia consist of:
- In-sufficient diet viz. iron-rich foods
- Blood losses due to heavy menstruation, different types of ulcers, many internal bleeding
- Increased requirement of iron during pregnancy period, growth spurts or any type of physical training
Q3: Signs/symptoms of iron deficiency anemia?
Ans. Typical symptoms are as follows:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Pale or yellowish skin
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Cold hands
- Feet Brittle nails
- Hair loss
Q4: Is there any category of people who are at risk due to iron deficiency anemia?
Ans. Different groups having risk for iron deficiency anemia as mentioned below:
- Women with heavy menstrual periods
- Pregnant women Infants and young children
- Mineral deficient diets among people who strictly consume non-meat food as a vegetarian or a vegan person
- Having some chronic diseases or gastrointestinal conditions if any
Q5: How iron deficiency anemia can be diagnosed?
Ans. Doctors diagnose iron deficiency anemia by performing blood testing which includes Assessment of these three elements:
- Hemoglobin levels as well as Hematocrit and Ferritin measurements together with Total Iron-Binding Capacity evaluation.
- How much red blood cells does one have in the blood system of humans
- Iron storage protein which is to know the Ferritin levels
- TIBC i.e. Total Iron Binding Capacity
Q6: How iron deficiency anemia treated?
Ans: Below are some steps:
- Iron for treating patients is either delivered through a pill or through an intravenous injection.
- Medical intervention requires incorporating spinach along with red meat and lentils and fortified cereals as part of your balanced diet.
- Treatment involves dealing with both issues related to blood loss and conditions that cause the body to not absorb nutrients well.
Q7: Is iron-deficiency anemia can be prevented ?
Ans: As mentioned below:
- Making sure you eat iron-rich foods to avoid problems.
- Absorption of iron increases if we take vitamin-c rich foods.
- During pregnancy period, Monitoring iron levels & know the actual status
Guideline of WHO for Iron Deficiency and its link as mentioned below: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/2021-dha-docs/ida_assessment_prevention_control.pdf
Thanks and Regards
About the Author – “Mr. Bibhu Ranjan Mund”, Master in Public Health (MPH) from IIHMR University, Jaipur (Rajasthan) has experience of 18 years in Public Health activities. Through “Lovely Health Tips-2025”, we share the evidence & experienced based health & wellness guides with solutions for every day well-being. More from Author
Disclaimer
This information is suggestive only and not a replacement for medical advice. For more detail, please visit to my website as mentioned below: