Last Updated on October 21, 2025 by
Substance Abuse in Adolescence — Young people in the adolescent phase typically try drugs and alcohol under the influence of peers while demonstrating interest in new experiences. Successful prevention is mostly based on educating parents, educating children and practicing early intervention methods. When risk factors are discouraged — sports and hobbies, support groups among peers — drugs is less likely. And at the community level, health care providers, teachers and counselors are working together to get at-risk teens to those services as quickly as possible.
The Reasons of Paying Attention to Adolescent Substance Abuse :
- In the developing adolescents, there is a higher susceptibility to change in the structure of the brain. Exposure to damaging elements throughout time can produce enduring brain damage that becomes more serious with each repeated encounter.
- Early initiation is associated with a poor prognosis, risk behavior susceptibility and social costs. Younger children and teenagers who start drinking are more likely to engage in behaviors that hurt them and other people.
- If caught in its early stages and treated appropriately, it can save the person, family, society, and health system from substantial costs.
- The use of Alcohol, Tobacco & Other Drugs (ATOD) and other risky behaviors typically begins in youth, and by late adolescence, a higher percentage of addiction disorders develop. Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) is likely to develop in people who begin drinking by the age of 16. Waiting twenty-five years increases likelihood protection to which matches the statistical risk across the general human population thereby demonstrating why first use should be postponed.
- Major drinking issues, such as alcoholism, which are usually linked to middle age, start to show up much earlier, in young adulthood and even youth.
- Teenagers are more susceptible to substance misuse because of the disruption of their educational schedules and diminished possibilities brought on by the COVID pandemic.
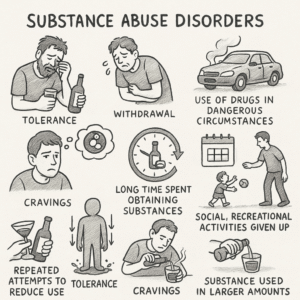
Substance Abuse Disorders
- Tolerance
- Removal
- Use of drugs in dangerous circumstances
- Crucial things that substance abuse has caused people to stop are also noted.
- They use products knowing the adverse effects
- Errors of omission failure to do important functions
- Cravings-
- Substances used were collected in short term durations.
- Unswerving ambition and barren effort to make abatement
- More often than intended, they now consume the substance and take more of it than planned.
- Tolerance describes the way a drug or alcohol’s reaction in the body diminishes for people who use it regularly. For this reason, the user must take a growing amount to feel the same effects they initially experienced.
- Experiencing certain physical or emotional changes as you reduce your use of an abused substance is what’s called withdrawal.
The Continuum of Drug Abuse :
Researchers might decide to use the drug as a test, join in because of what their peers are doing or simply to find out more about it.
Typical users :Dependent on a drug; always seeking it in an uncontrollable way Occasionally used
Occasionally used : Own the substance sometimes, either for social reasons or during specific stages, and have already passed the stage of experimentation.
Substance abuse among the teens is of various types:
Physical
- More sleep than normal
- Strange fatigue
- Sudden changes in body weight
- Water or bloody eyes
- Shaking
- Anxiety
- Being under the odor of alcohol or smoking
- Speech problem
- Unsteady footing
Emotional :
- Forceful
- Changes in a person’s mood
- Enthusiasm not found in day to day pursuits
- An individual finds it difficult to sustain the constant routines of action and time management.
- A student does not do their work assignments in a timely manner and separates themselves from both their family and their friends.
Social :
- They have often locked their doors
- Part of incomprehensible telephone activities is played alongside with subtle movements of other individuals.
- A person engages in theft and illegal activities together with evasive behavior and deception
- absences from school
- Being away much too long and demanding much and buying too much
- Using drugs with pals
Categories of Substances that are abused commonly:
Nicotine:
- Smoking through a cigarette, hookah, bidi or dhumti
- Khaini is bought & chewed with gutka.
- Naswar inhalation
- The use of khaini and gutka by chewing.
Cannabinoids:
- Hashish
- ganja
- charas
- bhaang
- marijuana
- pot
- Cannabinoids found in other forms
Opioids:
- Opium
- codeine
- buprenorphine
- heroin
- afeem
- smack
- brown sugar, etc.
Alcohol :
- Every type of wine
- beer
- distilled liquor, etc.
Sedatives:
- Seconals like barbiturates
- Valium, librium and others from benzodiazepines category
- Xanax
Volatile solvents or in solvents or volatile compounds
- Typewriter and a few other corrective fluids
- Hypo-dermic cement, glues, dry cleaners
- Glues and also many types of dry cleaners
- Nail polish removal type of nail products.
- You may use gasoline or kerosene as well
Hallucinogens:
- MDMA which people often call Ecstasy
- Mescaline
- LSD
Stimulants:
- Methamphetamine
- Cocain
- Amphetamine
- Atomoxetine

Many more which causes substance abuse:
Factors that protect
- Intellectual and physical development – Age wise
- Adoption of social abilities with Strong self-esteem
- From the family members, a Strong emotional support is a positive example
- Encouragement from scholastic achievement Interaction with peers in a healthy way and community Possibility of leisure and constructive engagement with culture
Factors at Risk:
- Genetic risks and prenatal/birth problems Insufficient nourishment
- Accessible easily
- When learning about Neglect, abuse or violence, a person’s self-esteem is often low.
- Family conflicts Caregiving that is inconsistent
- Failure in the classroom
- The act of bullying
- An unfavorable setting for learning
- At community, many disorganizations
- Discrimination and stigma
Substance Abuse: Working towards a good decision
- Talk openly with your teens about the advantages and limitations of staying involved with drugs, in the present and in the future.
- Present the upsides of their habits, being friendly and watchful of how you say it.
- Let them understand your reasons for caring why they are the way they are. Let them know that addiction to drugs stops them from using their talents and reaches their personal objectives.
- Let them see that drug addiction does not allow them to use their skills to reach their goals in life. Help teenagers learn about the situations and states that raise their chances of substance abuse.
- People should define their preferred changes alongside next steps.
The management of substance abuse involves the professionals to identify the risky conditions that could result in substance abuse:
Tactics of handling Substance Abuse: Learn to say no in a firm yet friendly manner:
Make use of the 4Ds method
- Delays
- Distractions
- Drink water
- Deep Breathing
People and external factors
- Places
- Occurrences
- Circumstances
- peer pressure
Internal elements:
- Adverse emotional mood
- hunger
- negative thoughts
- discomfort in the body
- fond memories of substance use
Various strategies in dealing with substance abuse: Increase your skills of saying no:
People should beware about the frequent use of pressure strategies by social groups.
- pleading
- comforting
- challenging
- threatening
- Anger
The examples when a person who practices assertiveness and rejection behavior can be found:
- My alcohol habit is final and I have broken it severally
- Since I am on medication that does not allow me to do so.
- I was about to go
- I had a headache
- Something necessary, and which can only be fulfilled by rising early.
Different assertiveness and refusal techniques to be ensured.
- Young people’s friendships shape them a lot • Help youth understand various pressure situations
- They might also do these activities by pretending to be in the moment.
- Idea generation about challenging circumstances involves participants to collaborate on responses they will utilize during such situations.
Approaches for Controlling Substance Abuse: Making a Supportive System.
- In addition to its other jobs, Safety Net assembles groups to help in the prevention of substance abuse.
- The support system may include: Parents, teachers, elders, friends, relatives, peers, counseling people, mentors, medical practitioners, and non-governmental organizations.
- Let the teenagers develop their own method for keeping safe.
Be engaged with nearby Communities, Families & friend.
For the purpose of preventing substance abuse
- An abnormal coping style in behavior or mood
- Getting to know parents while learning to speak clearly and teaching children discipline marks the essential elements of proper education.
For the control of drug abuse
- Encourage them to: Attach blame no moral failing to substance abuse.
- Attention needs for their day to day needs viz. health, medicine and nutrition.
- HDV+ provides information to people in the community on substance use concerns
- Show the teenager patience.
- Encouragement may be done for any little progress even it may tiny.
A Few Things Not To Do
- Focus on excuses for using drugs or choose to hide what the addiction is costing. Convey other regarding past substance abuse matters & issues.
- Keep harping on their faults, bicker and keep questioning their loyalty.
Helping people to learn about the damaging consequences of substance abuse
- Addiction is more common in teenagers.
- Give information to people about why substance abuse causes negative consequences.
- Give information for any misconceptions or untruths/unreal and un-biased regarding substance usage.
- Motivate community members to live away from drugs and keep them away from drug sources. Different types of outreach initiatives & session may be conducted to commemorate health days with adolescent people and school authorities/stakeholders to increase awareness.
- Required support may be provided with necessary encouragement to be done in the environment where people who are struggling with substance abuse.
Key Messages:
- The brains of teen people have increased levels of neuroplastic changes demonstrating sensitivity. When we keep encountering dangerous stimuli, a larger and more permanent change occurs in the brain.
- Use of Alcohol, Tobacco & Other Drugs (ATOD) and other high-risk behaviors typically begins in adolescence, and a greater percentage of addiction disorders manifest by late adolescence and young adulthood.
- The sooner that younger people try drinking, the more likely they are to act in risky ways toward themselves and others.
- If the initial use of substances is put off until age 25, then risk is reduced by 5%. Consequently, adolescent substance use may be seen in social, emotional or physical ways.
- The human body develops tolerance after it becomes less sensitive to influence from substances such as drugs and alcohol. Over time, the person can’t get the same effect with the same amount of the drug.
- Withdrawal describes human bodily physical together with psychological symptoms which evolve after stopping substance consumption or minimizing consumption levels.
- A safety net system acts as a network to help avoid substance use problems and their control. Some of the people who medical officers can help teens connect with include parents, teachers, elders, friends, family, friends, counselors, mentors, medical experts and non-governmental organizations. Attention must be paid to substance abuse during youth.

A small video from youtube on this topic is as mentioned below: https://www.youtube.com/embed/aMCXQ__c3F0?si=BmgagND_z3SBITis
FAQs:
Q1. What is adolescence substance abuse?
Ans. The dangerous misuse of alcohol tobacco marijuana prescription drugs and illicit drugs defines adolescent substance abuse in people who are age 10–19.
Q2. The substance abuse vulnerability of adolescents exists what underlying factors?
Ans. Due to their specific developmental period brain development adolescents take greater risks while surrendering to peer influence and conducting experiments. The combination of emotional distress and curiosity together with issues within the family create higher risk factors.
Q3. How can teenagers display their initial indications of drug abuse?
Ans. As mentioned below:
- Parent-teen ventilated interaction
- Drop in academic performance
- Secretive behavior or lying Mood or behavior changes along with shifts in eating habits or sleeping habits signal the start of substance abuse in teens.
- A teenager joins a brand new group of people to spend time with Smelling of smoke or alcohol
Q4. The most successful tactics for preventing teenagers from abusing substances would be which ones?
Ans. As below:
- Close relationships in the family and monitoring
- Good family relations and control
- Students need comprehensive drug education that happens frequently from an early age
- Fostering healthy behaviors such as sport or hobby
- School-based prevention programs
- Training decision making skills and refusal
Q5. When does prevention programming for substance abuse should start?
Ans. The prevention process should start during late childhood and early adolescence beginning at age 9 through 11 because experimentation usually emerges during this phase.
Q6. Schools as institutions must identify strategies to stop substance abuse among their students.
Ans. As below:
- Using programs based on scientific evidence for drug education
- Mental health services together with counseling are available to students
- Promoting good activities such as sport or interests
- Engaging parents with workshops and by sharing information
Q7. Parents participate in what ways to prevent substance use among their children?
Ans. A huge one. If parents regularly talk to their teens, the risk of drug use is very low for those teens. Establishment of clear boundaries together with clear expectations leads to success.
Q8. Do teen substance use behaviors receive significant influence from their peer relationships?
Ans. The influence peers have often matters a great deal to adolescents. Kids are more likely to use drugs when their friends are doing so which makes ensuring strong, healthy friendships especially important.
Guideline of WHO for Substance use and its link as mentioned below: Mental Health, Brain Health and Substance Use
Thanks and Regards
About the Author – “Mr. Bibhu Ranjan Mund”, Master in Public Health (MPH) from IIHMR University, Jaipur (Rajasthan) has experience of 18 years in Public Health activities. Through “Lovely Health Tips-2025”, we share the evidence & experienced based health & wellness guides with solutions for every day well-being. More from Author
Disclaimer
This information is suggestive only and not a replacement for medical advice. For more detail, please visit to my website as mentioned below:

