Last Updated on October 21, 2025 by
Dental Conditions in Children: Taking care of their teeth is vital for the total health of every child. The most common dental disorder in kids are cavities/tooth decay, which is usually due to excessive sugar intake and inadequate tooth brushing. Also, accumulation of plaque may lead to various gum diseases viz. gingivitis which causes swollen & bleeding gums. Malocclusion is a sign that the patient may require orthodontic treatment, while excess fluoride intake can lead to a condition related to tooth dis-colouration i.e. fluorosis. Kids also can have early tooth loss from either decay or trauma and tooth sensitivity.
Objective of Dental conditions in children:
- Know the signs of “Early Childhood Caries,” “Caries,” “Gingivitis conditions,” and their effects on a child’s health and well-being;
- How to prevent dental decay
- Comprehend how teeth decay
- Identification of tooth decay and other dental diseases with different conditions.
- Know how to prevent
How it starts?
- Streptococcus mutants
- Carbohydrates
- Acid formation
- De-mineralization
- Tooth Destruction
What Early Childhood Caries means?
- Severe and getting worse all the time
- Any primary tooth in a child aged six or less that has one or more decayed (cavitated or non-cavitated lesions), empty (cavitated) or filled tooth surfaces.
What to see ?
- Mothers caries status
- If the child complains of sensitivity to
- hot
- cold
- sweet
- food lodgment
- pain
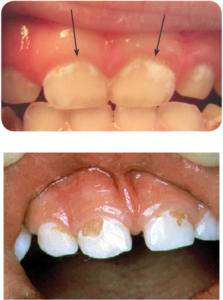
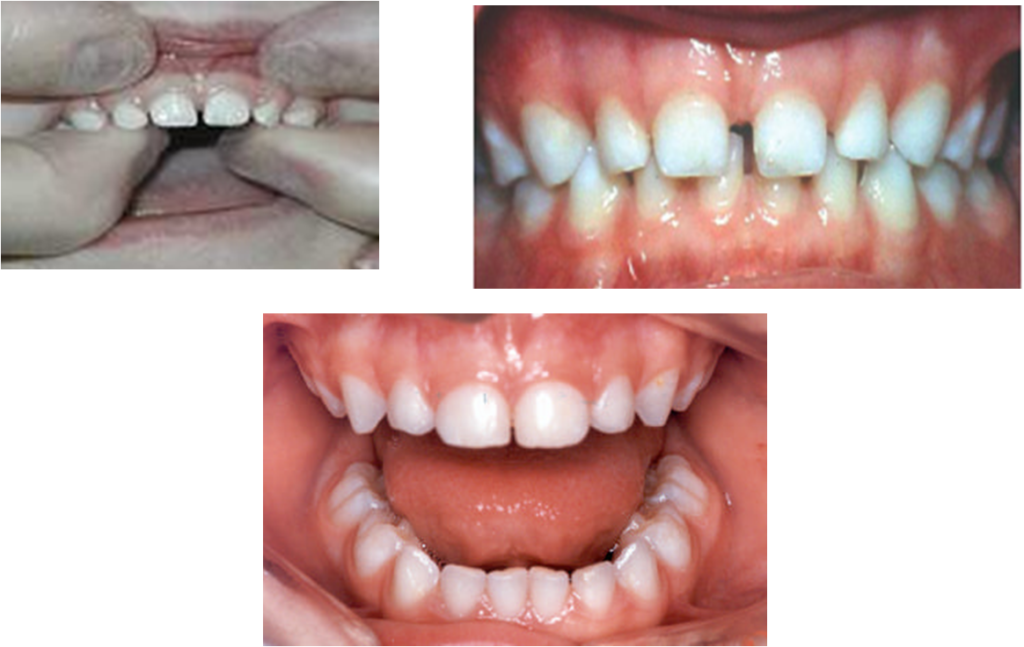
Check for Normal Healthy Teeth :
Now check the Early Signs of Decay in teeth of children & find-out White Spots:
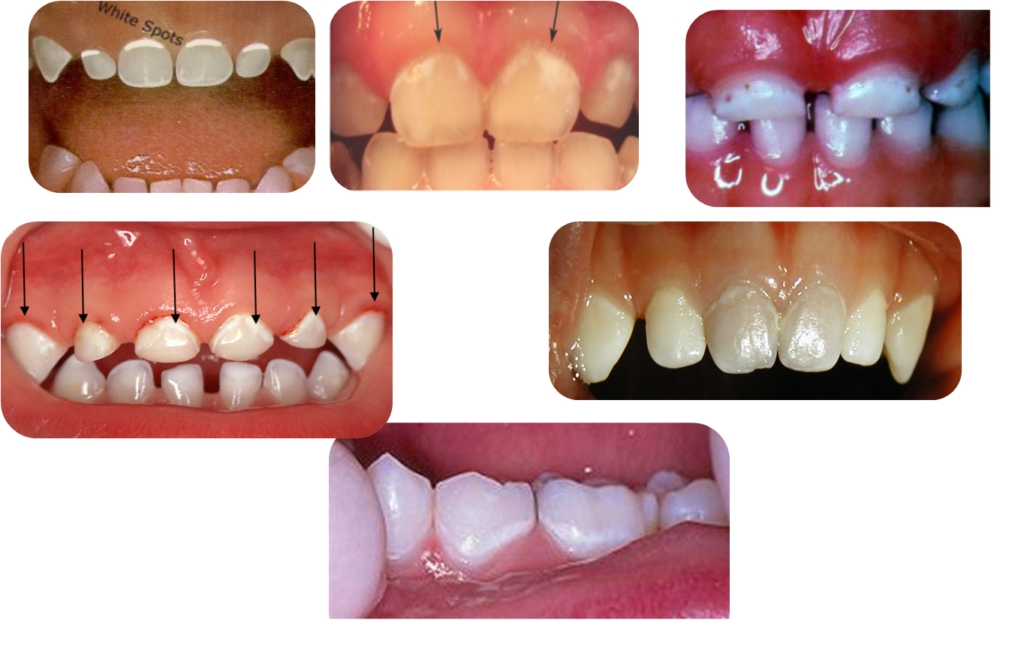
Later Signs of Decay- Brown Spots
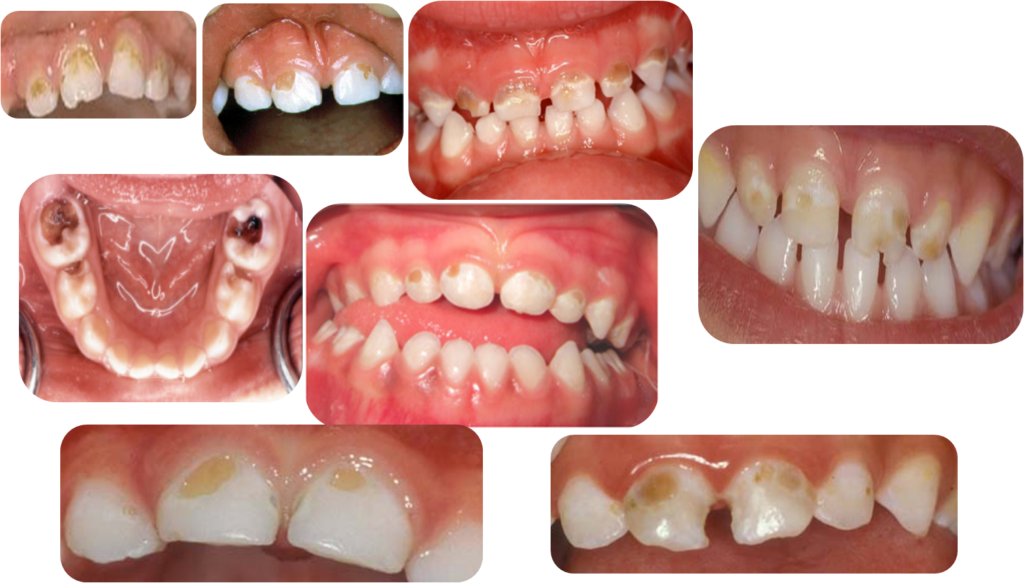
Advanced /Severe Decay :
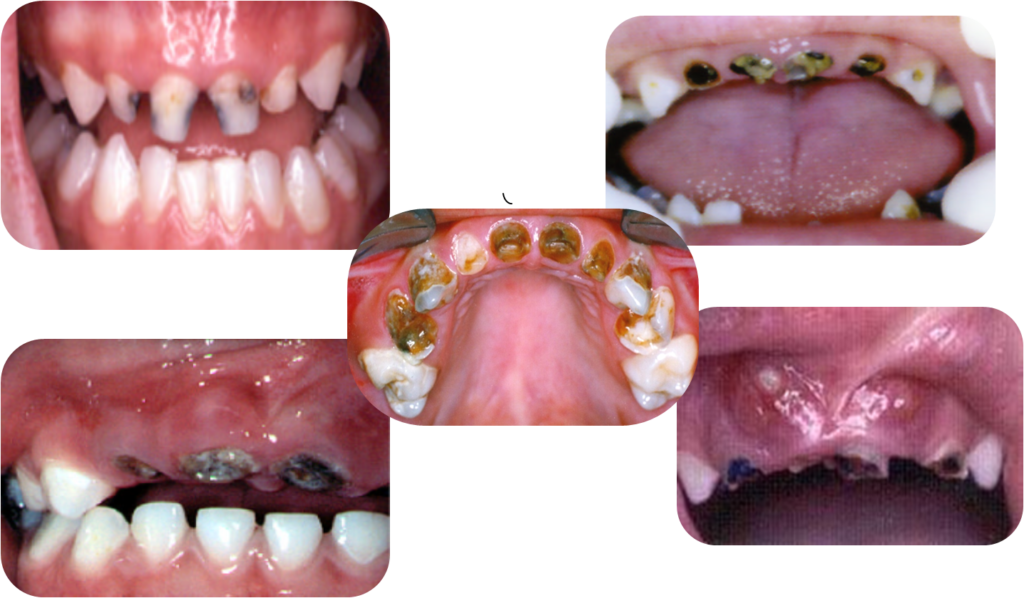
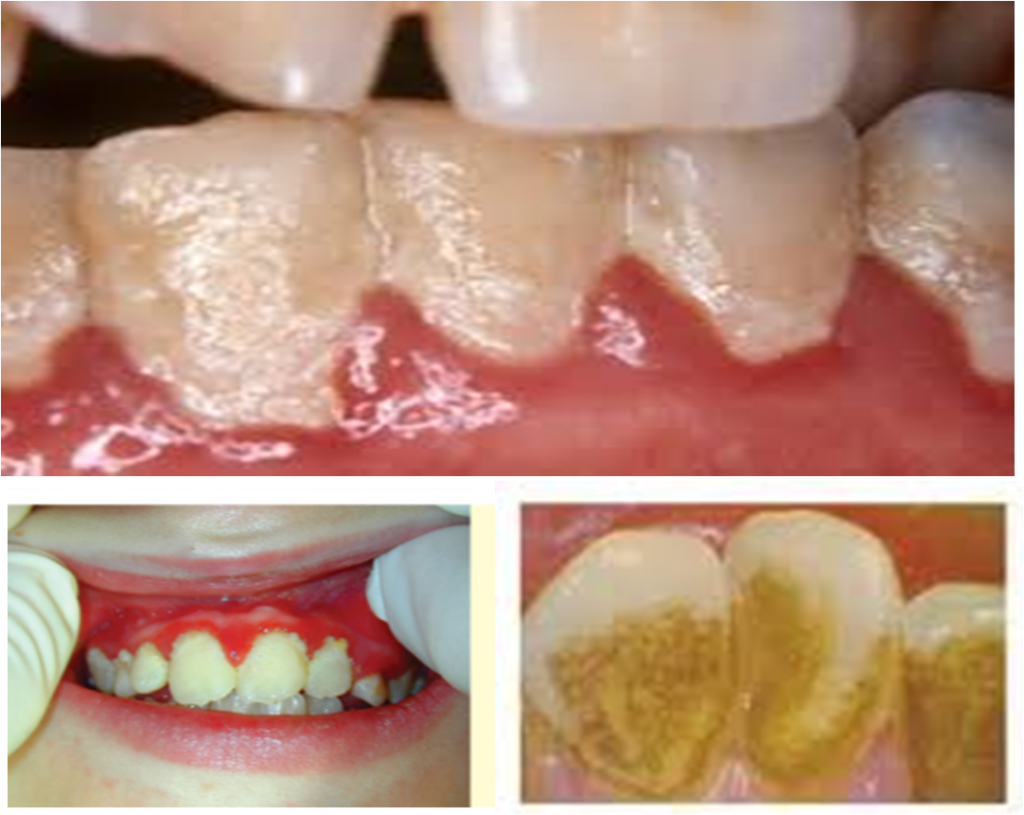
Check gums :
- Red
- Swollen-gums
- Bleeding gums
- Plaque / calculus
Early Childhood Caries leads to :
- The effects may include severe pain and easy transmission of infection.
- Dysfunction in speech and eating
- Delay of growth Adult teeth with crooked edges and a high risk of dental decay
- Dental treatment is more costly and also extensive
- Difficulty in taking food with eating & Dental Problems in Youngsters
- Having degradation of nutritional status of child
- Below average weight
- Disturbing how students learn in school and take part in activities
Early Childhood Caries is infectious and Transmittable disease :
Transferred to baby by the mother
- Advice from mother – Diet rich in calcium for promotion of teeth growth
- Mother should reduce microorganisms in her mouth by having good oral hygiene and brushing.
- Minimal risk of Early Child-hood Care in children
Infant feeding habits :
- The most effective way of feeding is breastfeeding.
- Don’t use bottles for Dental Conditions in Children
- No juice or milk to put to bed.
- Attempt to use a spoon and Katori.
- The first birthday is promoted with a drinking cup.
Be mindful of what you eat :
- Clear idea between-meal snacks & drinks.
- Limit eating
- Jalebi
- sweet
- Chips
- Kurkure
- Chockletts etc.
- It is not important what we will consume, but it is important how frequently we are consuming.
- Frequency of our diet plan matters more than its quantity we intake
- The acids you make last for 20 to 40 minutes.
- Water should be consumed after consuming sweets.
- For Sweet Bank: We should gather all the candy & to consume it on a specific day of the week only.
- Controlling consumption of sugar by self
- Eat sensibly and avoid cutting off sugar.
Prevent saliva from coming into contact with your child.
Damping the Saliva Exchange
- Keeping toothbrushes separate and not licking a dummy before handing it to a child
- Sharing food, beverages or utensils to be avoided among others.
- Do not allow the child to place his or her hand in the mouth of the caregiver.
Knowing about Oral Health:
- First tooth appears after being cleaned with moist cotton
- Once a month children must raise their lip at home to check for white/brown spots
- So, Parents should use a soft brush with fluoride toothpaste for brushing of their teeth & also for Dental Conditions in Children
- Swipe, under two years
- Pea size 2-5 year age
The right way to brush :
- Move the brush upwards and downwards in a back and forward movement with the brush applied to teeth slightly slowly.
Take home message for Dental Conditions in Children
- Our dental health relies on both our adult and our child’s baby teeth.
- Untreated decay in baby or early childhood teeth can cause a severe infectious disease.
- Having teeth, germs and carbohydrates in the mouth is how decay begins.
- Early childhood dental issues in children can all be stopped.
- On every child’s first birthday, don’t forget to take them for their first dental visit.
FAQs :
Q1. Which dental issues normally affect young children?
Ans. As below for Dental Conditions in Children
- Dental caries (tooth decay)
- Gingivitis (gum inflammation)
- Malocclusion (crooked teeth)
- Tooth erosion
- Dental trauma viz. accidents & injuries etc.
Q2. In the process of tooth decay which aspects specifically shape a child’s health status?
Ans. The onset of tooth decay creates several risks because it results in both painful conditions and infections which affect eating abilities while leading to sleep disturbances and speaking problems. The condition causes negative impacts on child growth alongside nutritional problems and learning difficulties.
Q3. The condition of a child’s teeth may cause adverse effects on both their self-confidence and academic performance at school.
Ans. A person with poor dental health often faces social embarrassment as well as speech problems alongside bad breath and experienced lower self-esteem because of both appearance and their breath problems.
Q4. At what stage in childhood should children start scheduling visits to the dentist?
Ans. Children are advised to attend the dentist at the age of less than one or when they erupt their first tooth
Q5. The main factor responsible for childhood tooth decay remains unknown.
Ans. As below for Dental Conditions in Children
- Sugary snacks/drinks
- Poor brushing habits
- Lack of fluoride
- Irregular dental check-ups
Q6. Do parents really need to put a lot of significance to the baby teeth as they will fall out anyway?
Ans. Yes. The temporary teeth also allow the children to continue with proper food habits as they also develop the power to speak and guide the adult teeth to find the right position. The early loss of teeth will negatively affect the proper alignment of permanent teeth during development.
Q7. What measures should I take to stop dental diseasess from developing in my child?
Ans. As below for Dental Conditions in Children
- Two brushing per day with fluoride toothpaste
- Limit sugary foods/drinks
- Ensuring periodical dental examination by Doctor
- Encourage a healthy diet
Q8. My child needs attention if he exhibits these dental warning signs.
Ans. As below for Dental Conditions in Children
- If your gums are red and swollen or they are bleeding, it may be gingivitis.
- It is not always clear how dental problems relate to a child’s nutritional status.
- Bad breathing
- Dis-coloration or spots on teeth
- Un-acknowledgement of food consummation
- Denial to bite on one side
Q9. What is the connection between dental issues and a child’s nutritional condition?
Ans. A child’s dental pain combined with tooth loss creates chewing dilemmas that results in inadequate nutrition and developmental problems.
Q10. Simultaneous problems in adulthood arise do poor oral health during childhood establish.
Ans. When a person neglects the care of his/her teeth, gum disease and infections may arise, resulting in early tooth loss.
Guideline of WHO for Dental condition and its link as mentioned below: https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/ending-childhood-dental-caries-who-implementation-manual
Thanks and Regards
About the Author – “Mr. Bibhu Ranjan Mund”, Master in Public Health (MPH) from IIHMR University, Jaipur (Rajasthan) has experience of 18 years in Public Health activities. Through “Lovely Health Tips-2025”, we share the evidence & experienced based health & wellness guides with solutions for every day well-being. More from Author
Disclaimer
This information is suggestive only and not a replacement for medical advice. For more detail, please visit to my website as mentioned below:

